Introduction
3D printing is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we manufacture products. It has opened up new possibilities for designers, engineers, and hobbyists alike. However, with so many different types of 3D printers available, it can be challenging to choose the right one for your needs. For the desktop 3D printers, the most of it you can see are FDM printers.
The common FDM 3D printer you can see includes slinger 3D printer and CoreXY printer. They are all Cartesian 3D printer. In this article, we will explore the meaning of the two 3D printer conceptions.

Overview of FDM 3D Printing Different Mechanisms
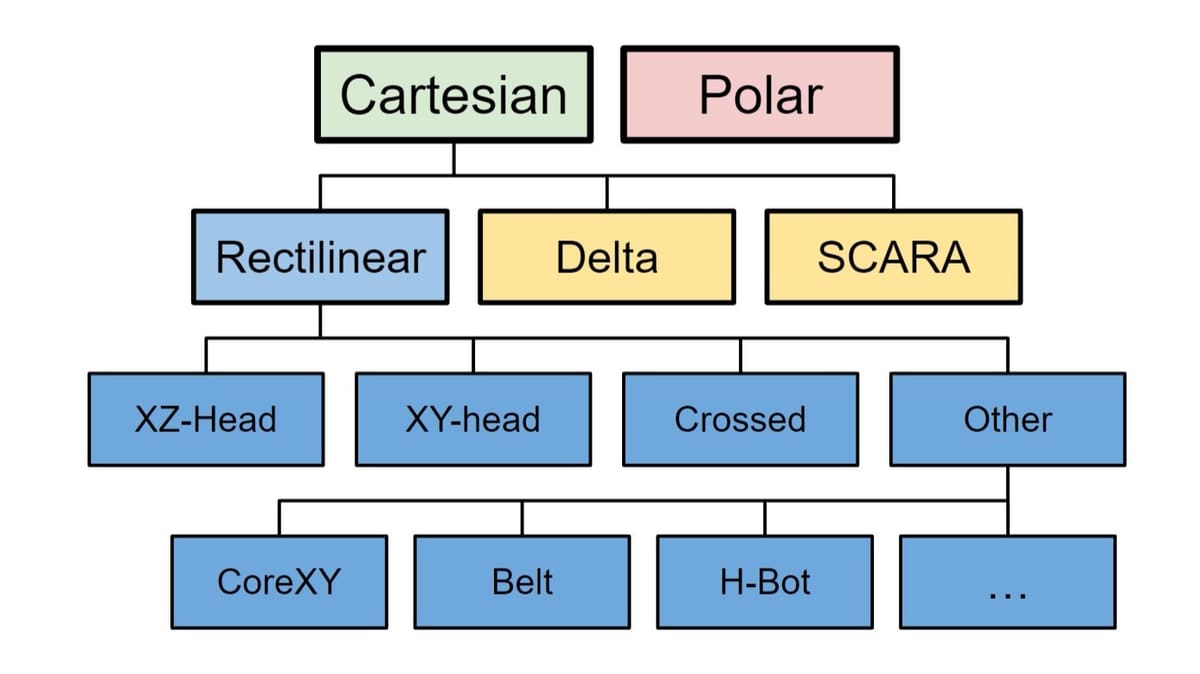
Cartesian 3D printer is a main category of 3D printer, it cover almost of the FDM 3D printer except the polar 3D printer. The CoreXY 3D printer is the most popular 3D printer in the market and many 3D printer manufacturers are developing new CoreXY 3D printers. There are more than 10 models of CoreXY 3D printer was released in 2024. In addition, the new comers are swarm into the market in 2025.
Cartesian 3D Printers
It use X, Y, and Z axes to move the print head and bed. So, it also be called “rectilinear” printers. They are the most common type of 3D printer and are known for their simplicity, reliability, and ease of use. Examples of Cartesian 3D printers include Creality Ender 3 (bed slinger), Kingroon KP3S Pro V2 (cantilever) and Bambu Lab P1P(CoreXY).
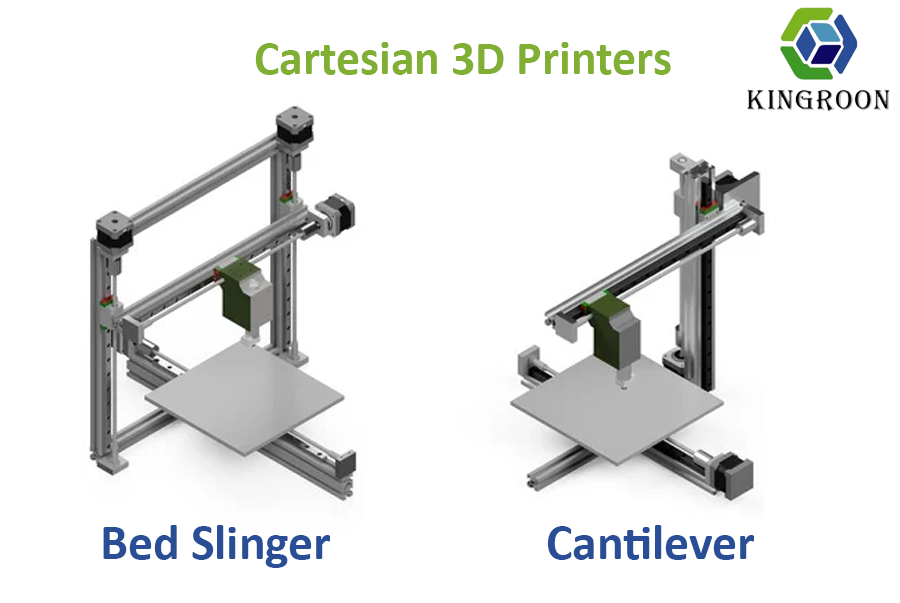
Figure 1 Source: mdpi.com
In a bed slinger mechanism, the print bed moves in the Y direction, while the print head moves in the X and Z directions which always have dual guides. This mechanism is known for its simplicity and ease of use, making it the most popular choice.
On the other hand, in the cantilever mechanism, the print bed typically moves in Y axis, and the extruder moves along X and Z axes. This design often sees the extruder mounted on a single arm or a beam that extends out, with no support on the opposite end, resembling a cantilever.
A special kind of Cartesian 3D printer is Delta 3D printer. The hot bed of this printer is round and fixed at the bottom of printer.
Cartesian printers are easy to use and maintain, making them ideal for beginners. However, they are slower than other types of 3D printers and have limited build volumes.
CoreXY 3D Printers
They use a belt-driven system to move the print head in the X and Y directions. The print bed moves only in the Z direction. This system allows for faster and more accurate printing, making CoreXY printers ideal for printing complex geometries. However, they are more expensive and difficult to set up than Cartesian printers. An example of a CoreXY 3D printer is the Kingroon KLP1.
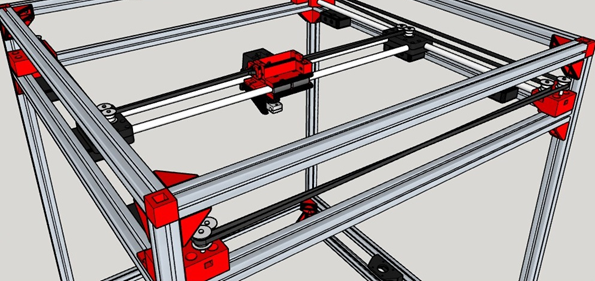
Figure 2 source: openbuilds.com
Comparative Analysis: Motion System Differences
Cartesian
For bed slinger 3D printers, they work on a straightforward principle where each axis (X, Y, and Z) moves independently. This design is simple and easy to understand, making these printers a go-to for many.
For Delta 3D printer, its print nozzle move to a position by control 3 connecting rods. The precision of this motion system is high. So, it can print at high-speed.
CoreXY
CoreXY printers use a more complex system with belts that control the X and Y axes simultaneously. This design allows for quicker and more precise movements but can be harder to grasp and set up initially.
Impact on Print Quality and Speed:
Cartesian
The independent movement of axes in Cartesian printers can sometimes lead to slower print speeds, especially for larger objects. However, they generally maintain a good level of print quality.
CoreXY
The coordinated movement system of CoreXY printers allows for faster printing without sacrificing quality. The reduced weight on the moving parts also leads to less vibration and smoother prints.
Cost Considerations Initial Purchase Price:
Cartesian
For bed slinger and delta 3D printer, it less expensive due to their simpler design and wider availability.
CoreXY
Tend to be more costly upfront because of their complex design and the precision components involved.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Cartesian
May incur lower maintenance costs but can have higher operational costs over time due to wear and tear, especially on models with moving beds.
CoreXY
While potentially more expensive to maintain due to their complex belt system, they often feature durable components that can result in lower long-term operational costs.
Performance and Capabilities Print Speed and Accuracy
Cartesia
Offers reliable accuracy but may lag in speed compared to CoreXY models.
CoreXY
Excels in both speed and accuracy, making it suitable for projects requiring high detail in shorter times.
Volume and Build Area Limitations
Cartesian
Often have a larger physical footprint for a given build volume due to the need for clear paths for each axis's movement.
CoreXY
Can offer larger build volumes in a more compact machine size because the print head moves more efficiently.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Cartesian 3D Printers
Pros:
● Simpler design for ease of use and maintenance.
● Generally, more affordable with a wide range of options.
● Good accuracy and quality for most applications.
Cons:
● Slower print speeds on larger prints.
● Larger physical size for equivalent build volumes.
● Potential for more vibration and noise at high speeds.
CoreXY 3D Printers
Pros:
● High-speed printing without losing print quality.
● Compact and efficient design for the same or larger build volumes.
● Reduced vibrations lead to smoother prints.
Cons:
● Higher initial cost and potentially steeper learning curve.
● More complex assembly and maintenance.
● Limited options available compared to Cartesian printers.
Case Studies: In-Depth Look at Cartesian and CoreXY Printers
To understand the practical differences between Cartesian and CoreXY 3D printers, let's examine three popular models: the Ender 3 with its bed-slinger design, the Kingroon KP3S Pro V2 featuring a cantilever setup, and the CoreXY model Kingroon KLP1. These examples highlight the real-world application, advantages, and challenges associated with each design.
Cartesian Examples
Creality Ender 3 (Bed-Slinger Design)
Creality Ender 3 (Bed-Slinger Design) is a popular and affordable 3D printer that offers a print volume of 220X 220 X 250mm and a heated bed with a removable magnetic surface. It has a simple and open design with a sturdy aluminum frame. It is compatible with various materials, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and wood.

Figure 3 source: creality.com
Price: Priced at $189.00 on the official website.
Pros and Cons in Practice:
Pros:
● Large and consistent print quality with a spacious print area and a stable frame.
● Easy to assemble and operate with clear instructions and a simple interface.
● Affordable and customizable with a low price and a large community of users.
● Reliable and convenient with a power resume function and a removable print surface.
Cons:
● The print bed may need frequent manual leveling and adjustment due to the bed-slinger design.
● The vibration may affect the print quality in high printing speeds specially with the bed movements along Y axis.
Kingroon KP3S Pro V2 (Cantilever Design)
Kingroon KP3S Pro V2 (Cantilever Design) is a fast-printing 3D printer that comes with Klipper firmware installed, which allows for high-speed and high-quality printing. It has a compact design with a decent print volume of 200 X 200 X 200mm and a heated bed with a PEI sheet. It also features linear rail guides on all axes, an all-metal extruder with a 9.5:1 gear ratio, and an integrated WIFI module for remote control. It is suitable for printing various materials, including PLA, PETG, and TPU.
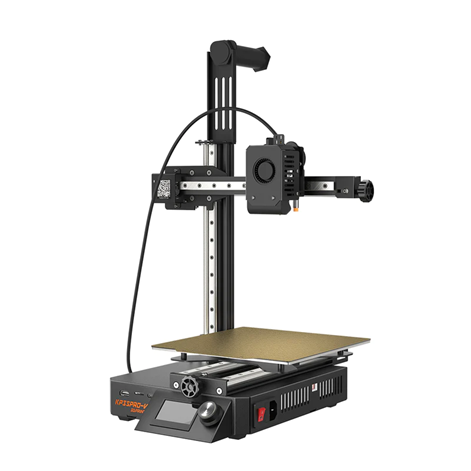

Figure 4 kiingroon.com
Price: Priced at $249 at the official website.
Pros and Cons in Practice:
Pros:
● Fast and stable printing with Klipper firmware and linear rail guides.
● Easy to set up and use with 95% pre-assembly and a user-friendly interface.
● Versatile and reliable with a direct drive extruder and a wide range of compatible materials.
● Quiet and safe with TMC2225 stepper drivers.
● Convenient and flexible with WIFI connectivity and resume printing function.
Cons:
● The print bed may need frequent leveling and calibration due to the cantilever design.
● The fan noise may be loud when printing at high speed.
● The Cantilever design may be affected with some vibration at very high speeds as it is supported only from one side.
CoreXY Example
Kingroon KLP1 (Core XY design)
Kingroon KLP1 (Core XY design) is a high-performance 3D printer that features a CoreXY structure, linear rail guides, and Klipper firmware. It has a large print volume of 210 X 210 X 210 and a heated bed with a steel sheet. It also features a 5:1 gear ratio extruder, an all-metal hotend, and a WIFI module for remote control. It can print various materials, such as PLA, PETG, nylon, and CF.
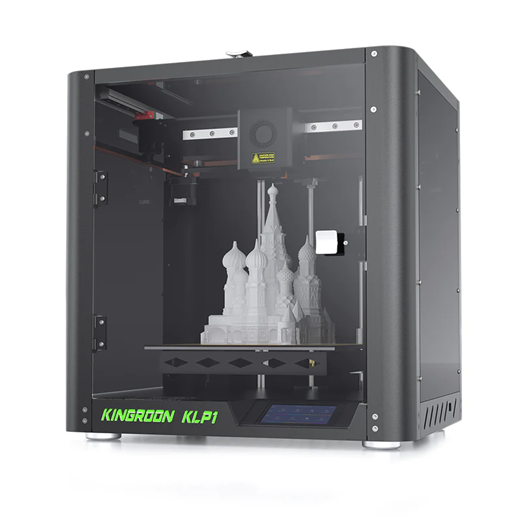

Figure 5 source: kingroon.com
Price: Priced at $379 at the official website.
Pros and Cons in Practice:
Pros:
● Fast and accurate printing with CoreXY structure and linear rail guides.
● Easy to set up and use with 95% pre-assembly and a user-friendly interface.
● Powerful and versatile with a 5:1 gear ratio extruder and a wide range of compatible materials.
● Quiet and safe with TMC2209 stepper drivers.
Cons:
● The fan noise may be loud when printing at high speed.
● The Core XY design can be more complex to maintain and calibrate compared to traditional Cartesian printers. This might pose a challenge for beginners in 3D printing.
● The price maybe higher than the cartesian printers.
Conclusion
Choosing the right 3D printer, be it Cartesian or CoreXY, depends on the user's priorities. If affordability and ease of use are key, a Cartesian printer like the Kingroon KP3S Pro V2 is a great starter option, known for its reliability and straightforward design. For users prioritizing speed and print quality for complex projects, a CoreXY printer, such as the Kingroon KLP1, offers advanced capabilities and precision, though with a higher price tag and a bit more complexity in setup and maintenance. Each type serves different needs, making it important to consider what factors—cost, ease of use, print speed, and quality—are most important to your 3D printing goals.

